Excerpt
Comprehensive health assessments, including full body checkups, are crucial in preventive healthcare. They offer more than routine check-ups; they are a proactive approach for early detection and prevention of health issues. Such assessments identify current health problems and anticipate future risks, emphasizing the importance of early intervention. Full body checkups are vital for effective treatment and preventing conditions from escalating into more serious diseases. They embody the principle that timely preventive action is golden, especially in healthcare, where “time is heart.”
Introduction
Understanding Comprehensive Health Assessments
The Essence of a full body checkup
A full body checkup recommended by your doctor is a meticulously structured evaluation aimed at the early detection and prevention of potential health issues. These assessments are much more than routine check-ups; they are a proactive approach in healthcare, intricately designed to capture a complete picture of an individual’s health. The objective of a full body checkup is not only to identify existing health problems but also to foresee potential risks that might emerge in the future.
Why a full body checkup is Crucial
- Early Detection of Health Issues: One of the primary advantages of full body checkup is their ability to identify health concerns at an early stage, often before symptoms become apparent.
- This can lead to more effective treatment options and prevents health issues from developing into more serious conditions (such as lipid profile).
- Preventive Health Strategy: A full body checkup by your doctor is a cornerstone in preventive medicine. By evaluating various health parameters, they empower individuals and healthcare providers to take preemptive actions. This might include lifestyle changes, medication, or further testing to mitigate the risk of diseases.
- Personalized Health Insights: Every individual’s health profile is unique, and comprehensive health assessments acknowledge this by providing personalized insights. They take into account an individual’s medical history, family history, lifestyle, and other factors.
- Personalized Health Insights: Every individual’s health profile is unique, and comprehensive health assessments acknowledge this by providing personalized insights. They take into account an individual’s medical history, family history, lifestyle, and other factors.
- Holistic Health Evaluation: These assessments go beyond diagnosing diseases. They evaluate physical, mental, and emotional well-being, offering a holistic view of health. This approach ensures that all aspects of an individual’s health are considered, providing a more effective and integrated
health management plan.

- Empowering Individuals with Knowledge: Knowledge is power in healthcare. By providing detailed information about their health status, these assessments empower individuals to take charge of their health. Understanding their own health risks and conditions enables them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle, diet, and medical care.
- Facilitating Doctor-Patient Communication: Comprehensive health assessments provide a foundation for meaningful conversations between patients and healthcare providers. They offer a detailed health report that can be used as a starting point for discussing health concerns, treatment
options, and health goals.
How Comprehensive Health Assessments Work
A comprehensive health assessment typically involves several components, including but not limited to:
- Medical History Review: This is the first step, where detailed information about the patient’s past and present health conditions, family health history, lifestyle choices, and medication use is gathered.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted to check the overall health status. This may involve assessments of the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, neurological functions, and other vital organs.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the individual’s age, sex, family history, and lifestyle, a series of diagnostic tests may be recommended. These can range from blood tests to advanced imaging techniques.
- Risk Assessment: Part of the assessment is dedicated to evaluating the risk of future health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, or cancer, liver function test, kidney function test, based on the individual’s health data can help.
- Health Counseling and Recommendations: Post-assessment, individuals receive personalized advice on maintaining or improving their health. This might include recommendations for lifestyle changes, preventive measures, or follow-up tests can help.
Therefore, Comprehensive Health Assessments are an invaluable tool in modern healthcare, offering a depth of insight into an individual’s health that goes beyond the surface.
They play a pivotal role in early disease detection, prevention, and in fostering a proactive attitude towards health maintenance.
Key Elements of a Standard Comprehensive Health Assessment
Medical History Assessment
Detailed Physical Check-Up: This includes a thorough examination of various body systems, such as cardiac, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems. Measurements like blood pressure and heart rate are taken.
Blood Analysis:
Tests for cholesterol, blood sugar levels, lipid profile, liver and kidney functions, and a complete blood count (CBC) are conducted.
Urinary Analysis: This test checks for signs of diabetes, kidney disorders, and other conditions.
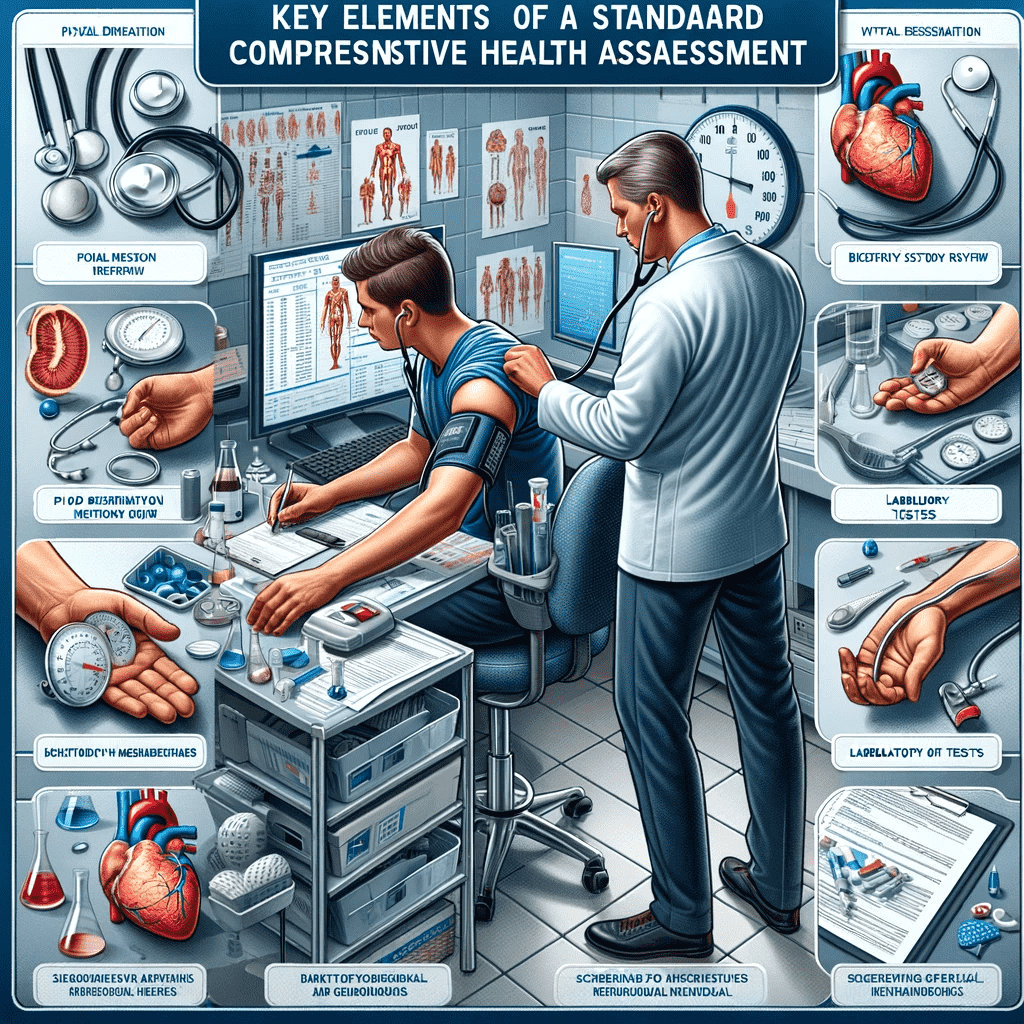
Diagnostic Imaging: Tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans may be recommended based on age and risk factors can help.
Cardiac Tests: An ECG (Electrocardiogram) is typically performed. In certain cases, a treadmill stress test or an echocardiogram may be conducted. If heart issues are suspected, speckle tracking echocardiography might be advised.
Detailed Breakdown of Common Assessment Components
Importance in Health Assessment
Physical Evaluation is essential for a complete health picture, helping detect subtle health issues and forming a basis for a personalized healthcare plan.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a fundamental, non-invasive diagnostic tool used in the assessment of cardiac health. It works by recording the electrical activity of the heart, capturing data crucial for the detection of a variety of cardiac conditions.
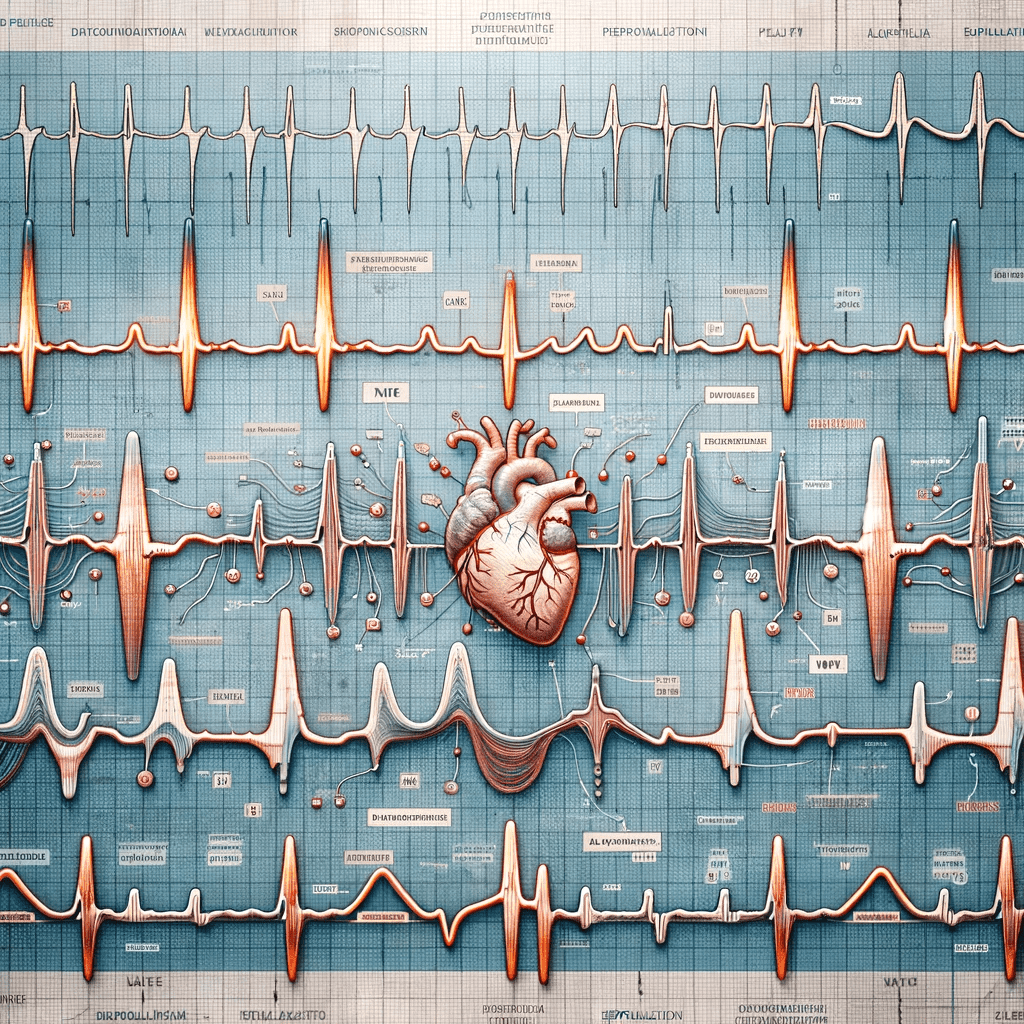
This simple yet effective procedure involves placing electrodes on the patient’s skin, which then pick up electrical impulses generated by the heart as it beats. These impulses are translated into waveforms, visually represented on a graph.
The ECG is can help in identifying arrhythmias, signs of ischemia, uncover hidden cardiac symptoms makes it a cornerstone in preventive cardiovascular care.
Treadmill Stress Test
Your doctor can suggest the Treadmill Stress Test, a vital diagnostic tool used to evaluate the performance of the heart under physical stress. This test is particularly insightful for diagnosing conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), where blood flow to the heart muscle is restricted due to narrowed or blocked arteries.

Throughout the test, the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) readings are continuously monitored. These readings provide crucial information about how the heart responds to increased physical activity.
Changes in the ECG pattern during exercise can signal the presence of ischemia – reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Similarly, abnormal changes in blood pressure and heart rate can also indicate cardiac issues.
Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a group of non-invasive tests that play a crucial role in assessing the health and functionality of the lungs. These tests measure lung volume, capacity, rates of airflow, and gas exchange, providing comprehensive data about the respiratory system.
PFTs are particularly vital in diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions such as asthma, where airways become narrow and swell, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a group of lung conditions that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe.
PFTs are used to monitor the progression of lung diseases and to assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies. They are also essential for preoperative evaluation, especially before major surgeries, to ensure patients’ lungs are healthy enough for anesthesia and the surgery’s stress. Regular PFTs can help in early detection of lung diseases, enabling timely intervention and better management of the patient’s condition.

Abdominal Ultrasound
This painless procedure helps in identifying issues in abdominal organs, such as liver disease, gallstones, or kidney stones.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is an advanced, non-invasive imaging test that offers a detailed visualization of the heart’s structure and function. Ultrasound waves produce real-time images of the heart to observe heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels in action. This technique is crucial for diagnosing a range of cardiac conditions, from valve disorders and heart muscle diseases to congenital heart defects.
It helps in detecting abnormalities like heart enlargement or impaired pumping function, and can also identify fluid accumulation around the heart. The echocardiogram is a key diagnostic tool in cardiology, providing essential information for the effective management and treatment of heart diseases.
Speckle Tracking Echocardiography
Speckle Tracking Echocardiography (STE) is a sophisticated imaging technology that enhances traditional echocardiography by analyzing the motion of ‘speckles’ seen in the heart muscle tissue. These speckles, unique acoustic markers created by ultrasound waves, allow for a highly detailed evaluation of the heart’s motion and deformation. STE provides cardiologists with an in-depth understanding of heart mechanics, aiding in the detection of subtle cardiac dysfunctions that conventional echocardiography might miss.
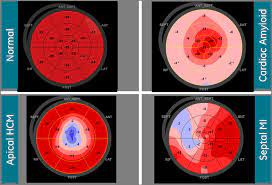
Comprehensive blood tests
Vital for gauging overall health. They include tests like peripheral smear, lipid profile, fasting blood sugar, blood sugar after a meal, blood sugar during a Glucose Tolerance test, lipid profile, liver and kidney function tests, and others.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is a simple yet informative test that examines a urine sample for various health indicators.
Conclusion

Comprehensive health assessments are key in preventative healthcare. They provide a complete overview of an individual’s health, allowing for early detection and management of health issues. Regular check-ups are fundamental to maintaining good health, longevity, and enhancing life quality by ensuring health concerns are addressed promptly.