Understanding Holter Monitoring of the Heart.
Imagine you’re trying to catch a glitch in your computer, but it only happens now and then. If you were to observe the computer only for a few minutes, chances are, you’d miss it. Similarly, when doctors want to understand the heart’s behavior over an extended period, they use a special tool called a Holter monitor.
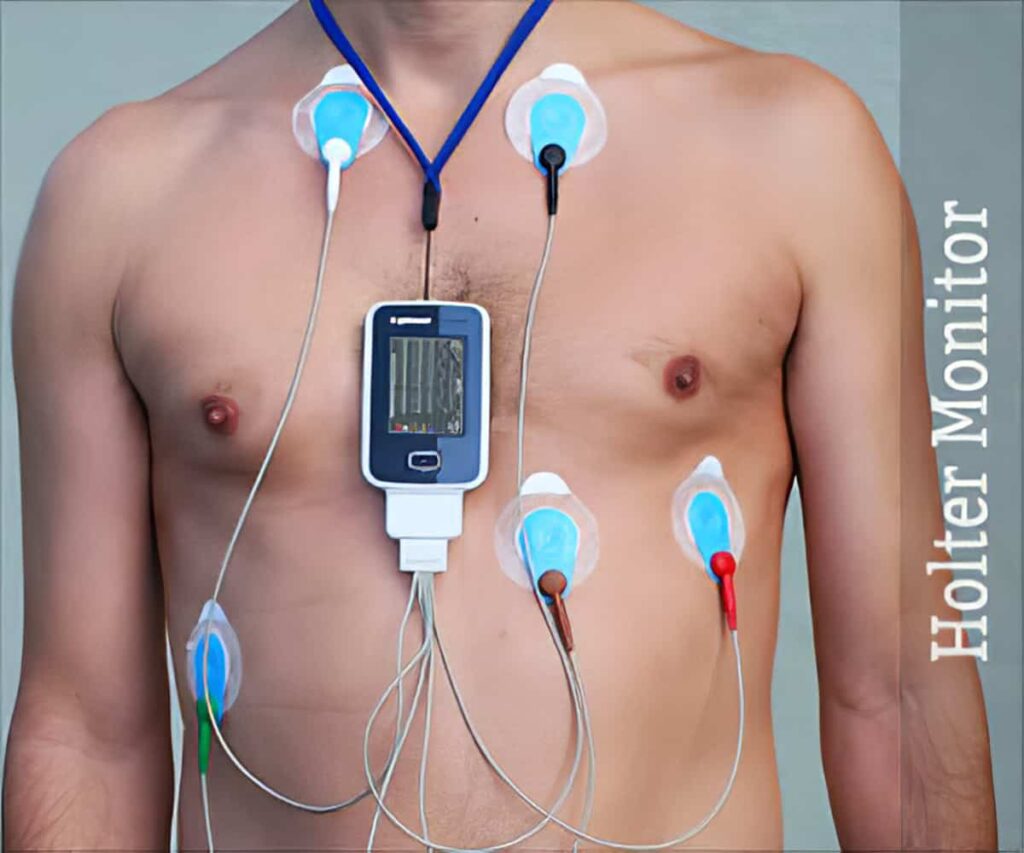
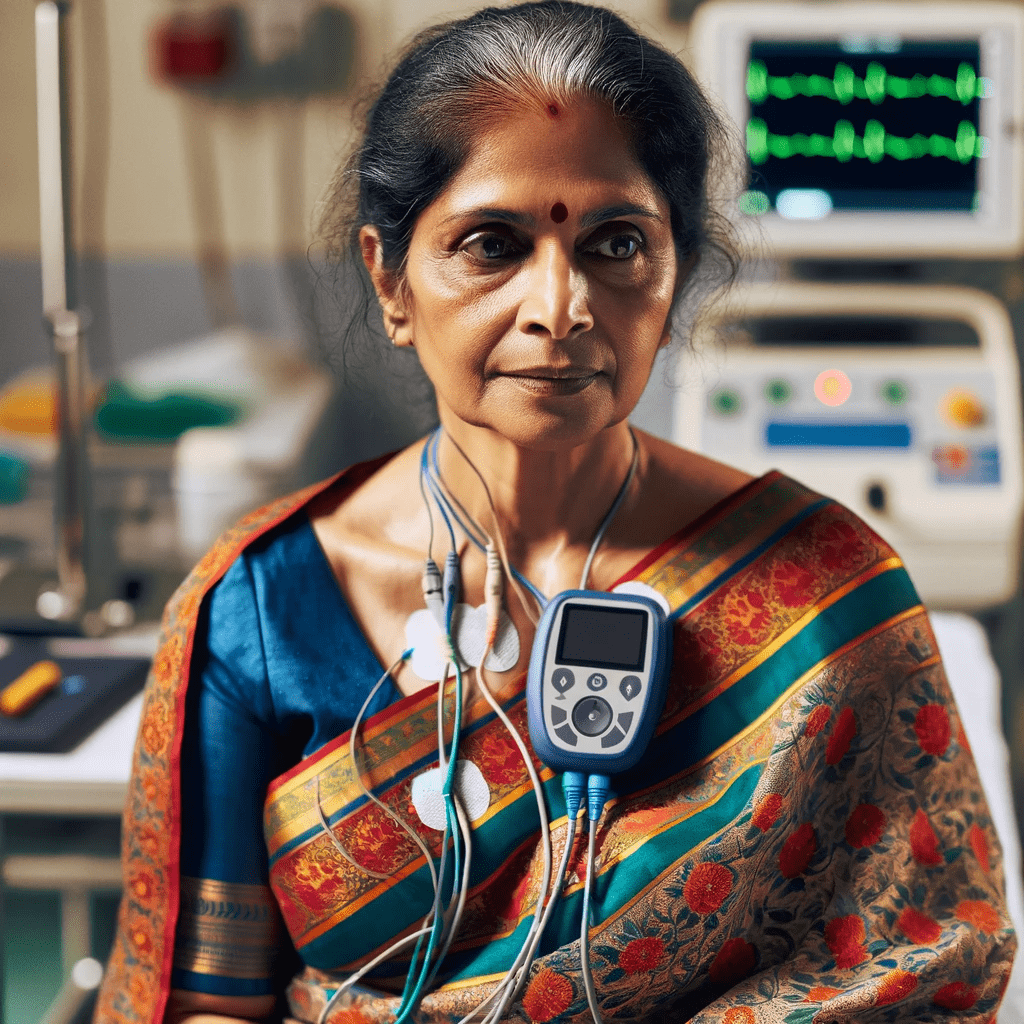
Holter monitoring, an essential diagnostic tool in cardiology, offers several key benefits:
- Continuous Heart Monitoring: Holter monitors continuously record heart activity for 24-48 hours, capturing irregularities that might be missed during a brief ECG exam.
- Detection of Arrhythmias: It is particularly effective in detecting arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats that occur sporadically and may not be present during a standard ECG test.
- Assessing Symptoms: Holter monitoring helps correlate symptoms like dizziness, palpitations, or fainting spells with heart activity, providing clues about their cardiac origin.
- Evaluating Treatment Efficacy: It is invaluable for assessing the effectiveness of cardiac treatments, such as medications for arrhythmias or pacemaker function.
- Identifying Silent Ischemia: The monitor can detect episodes of silent ischemia – periods when the heart muscle isn’t receiving enough oxygen without causing symptoms.
- Risk Assessment: For patients with a history of heart attack or heart disease, Holter monitoring can assess the risk of future cardiac events.
- Monitoring Post-Surgery: It’s often used to monitor heart function in patients recovering from heart surgery or a heart attack.
- Uncovering Sleep-Related Issues: Holter monitoring can identify heart-related issues that occur during sleep, such as bradycardia or tachycardia.
- Portable and Non-Invasive: As a portable device, it allows patients to go about their daily activities without hospitalization, making it a convenient diagnostic tool.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: It provides a comprehensive dataset for physicians to analyze, leading to a more accurate and complete understanding of a patient’s heart health. (Read More…)
FAQs
I am 40 years and frequently have palpitations in the chest. My doctor suggests a Holter Monitoring. Is it necessary?
Experiencing frequent palpitations at 40 years old can be concerning, and it’s important to get a proper evaluation to determine the cause. Your doctor’s suggestion to undergo Holter monitoring is likely based on the need to assess these symptoms more thoroughly. Here’s why Holter monitoring might be necessary in your case:
- Continuous Recording: Unlike a standard electrocardiogram (ECG) that records the heart’s activity for a few seconds, a Holter monitor records continuously over a 24-48 hour period (or longer, in some cases). This increases the likelihood of capturing your palpitations.
- Identifying Arrhythmias: Palpitations can be caused by heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias). A Holter monitor can help identify if you are experiencing arrhythmias, and if so, what type.
- Correlating Symptoms with Heart Activity: It allows for correlating your symptoms (like palpitations) with your heart’s electrical activity at the exact time they occur.
- Risk Assessment: If you have other risk factors for heart disease (like high blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease), the monitor can help assess your overall cardiac risk.
- Guiding Treatment: Depending on the findings, it can guide your doctor in choosing the best treatment approach, whether it’s medication, lifestyle changes, or further testing.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing the exact cause of your palpitations can provide peace of mind and help reduce anxiety about your symptoms.
Remember, while Holter monitoring is a valuable diagnostic tool, it’s just one part of a comprehensive cardiac evaluation. Your healthcare provider will consider your entire clinical picture, including your medical history, physical examination, and other tests as needed, to make an informed decision about your care. It’s always a good idea to discuss any concerns or questions you have with your doctor to understand the reasoning behind their recommendations
What is the concept behind Holter monitoring? Why is it superior to a few ECGs taken on the same day?
Holter monitoring is based on a concept quite different from standard Electrocardiography (ECG) testing, offering several advantages, particularly in its approach to capturing and analyzing heart rhythm over an extended period. Here’s an overview of the concept and its superiority compared to a few ECGs taken on the same day:
- Continuous Long-Term Monitoring: The fundamental concept behind Holter monitoring is continuous recording of the heart’s electrical activity over an extended period, typically 24-48 hours, and sometimes up to 72 hours or longer. This long-term monitoring is crucial for detecting irregularities that might not occur during the brief window of a standard ECG.
- Capturing Intermittent Arrhythmias: Many cardiac arrhythmias are intermittent and might not occur during a short ECG recording. Holter monitoring increases the likelihood of capturing these sporadic events by continuously monitoring the heart rhythm throughout various daily activities and rest periods.
- Correlation with Symptoms: Holter monitoring allows for the correlation of heart rhythm with symptoms experienced by the patient. For example, if a patient experiences palpitations, dizziness, or fainting spells, the Holter monitor can help determine if these symptoms are related to heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Treatment: For patients who are already on medication for heart conditions, Holter monitoring can assess the effectiveness of treatment. It helps in determining if the medication is working properly to regulate the heart rhythm.
- Detecting Silent Ischemia: Unlike a standard ECG, which might miss brief periods of ischemia (lack of blood flow to the heart muscle), a Holter monitor can detect these episodes, which often occur without causing symptoms.
- Risk Stratification: Holter monitoring provides valuable data for risk stratification in patients with known heart conditions, such as post-myocardial infarction (heart attack) patients. It can help in predicting the risk of future cardiac events like heart attacks or sudden cardiac death.
- Recording During Normal Activities: Holter monitors record the heart’s activity during normal daily routines, providing a more representative assessment of the heart’s function under typical conditions, rather than just in a clinical setting.
- Detailed Analysis: The data collected is extensive and allows for a detailed analysis of heart rhythms over the monitoring period. This comprehensive data is invaluable for diagnosing complex arrhythmias.
In summary, Holter monitoring’s superiority lies in its ability to provide a detailed and continuous picture of the heart’s electrical activity over a significant period, capturing events that might be missed during the short snapshots provided by one-time ECGs. This makes it an essential tool in diagnosing and managing various cardiac conditions.
What time period should I be subjected to this Holter test?
The duration for which you should wear a Holter monitor largely depends on the nature of your symptoms and your doctor’s specific diagnostic goals. Commonly, Holter monitoring periods are as follows:
- 24-Hour Monitoring: This is the most standard duration. It’s typically sufficient to capture daily variations in heart rhythm, including any abnormalities that might correlate with your symptoms like palpitations.
- 48-Hour Monitoring: If your symptoms are less frequent, a 48-hour period might be recommended. This extended duration increases the chances of detecting intermittent arrhythmias or correlating symptoms with heart rhythm abnormalities.
- 72-Hour or Longer: In some cases, especially when symptoms are sporadic, your doctor might recommend wearing the monitor for 72 hours or even longer. This is less common but can be necessary for a thorough assessment.
- Event Monitors: If your symptoms occur infrequently (less than once a week), your doctor might suggest an event monitor instead. Event monitors are worn for longer periods (up to a month or more) and are activated by the patient when they experience symptoms.
Your doctor will decide the appropriate duration based on factors like:
- Frequency of Symptoms: If your symptoms are daily, a 24-hour monitor might suffice. Less frequent symptoms might require longer monitoring.
- Diagnostic Goals: The duration may vary depending on whether the aim is to diagnose a condition, assess the severity of known heart disease, or evaluate treatment efficacy.
- Previous Test Results: If prior ECGs or other tests have been inconclusive, longer monitoring might be needed for a definitive diagnosis.
It’s important to wear the monitor for the entire recommended period without interruptions to ensure the most accurate and comprehensive data collection. Your doctor will provide specific instructions on how to use the monitor and what activities to record during the monitoring period.
Can I continue to be normal during a Holter Test?
Yes, you can and should continue with your normal daily activities while undergoing a Holter monitor test. The primary purpose of Holter monitoring is to record the electrical activity of your heart during routine activities, as this provides valuable insights into how your heart functions on a typical day. However, there are a few considerations and guidelines to keep in mind:
- Avoid Water Activities: Since the Holter monitor is an electronic device, it’s important to keep it dry. Avoid swimming, bathing, or showering while wearing the monitor. Some newer models might be water-resistant, but it’s best to confirm with your healthcare provider.
- Physical Activities: You can engage in regular physical activities unless instructed otherwise by your doctor. However, excessive sweating might loosen the electrodes, so it might be wise to avoid extremely strenuous exercises.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Try to avoid areas with strong electromagnetic fields, such as metal detectors or high-powered electrical equipment, as they can interfere with the monitor.
- Sleep Considerations: Wear the monitor while sleeping. It can be helpful for the doctor to see your heart’s activity during sleep. If the monitor is uncomfortable, try to position it in a way that doesn’t disrupt your sleep.
- Medications and Diet: Continue taking any prescribed medications unless your doctor advises otherwise. There are generally no dietary restrictions, but it’s a good idea to keep your diet consistent with what you would normally eat.
- Diary of Activities and Symptoms: You will likely be asked to keep a diary of your activities and any symptoms you experience while wearing the monitor (such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or palpitations). This helps correlate specific activities or times with any changes in your heart rhythm.
- Clothing Considerations: Wear comfortable clothing that allows easy placement of the monitor and electrodes. A shirt that buttons in the front can be more convenient for wearing and adjusting the monitor.
- Avoiding Skin Irritation: The adhesive used to attach the electrodes might cause skin irritation for some people. If you have sensitive skin, mention this to your healthcare provider.
Remember, the more typical your activities are during the monitoring period, the more representative the data will be of your heart’s usual activity. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. If you have any specific concerns or questions about your activities during the Holter monitoring, it’s best to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Should I be hospitalized for a Holter Test?
No, hospitalization is not required for a Holter monitor test. One of the key advantages of Holter monitoring is that it’s a non-invasive, ambulatory procedure, meaning it’s designed to be carried out as you go about your normal daily activities.
Here’s what typically happens:
- Setup Appointment: You will have a brief appointment at a hospital or clinic to have the Holter monitor fitted. This usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes.
- Wearing the Device: After the setup, you are free to leave the hospital or clinic. You’ll wear the Holter monitor, a small, portable device, for a set period, usually 24-48 hours, though sometimes longer if directed by your doctor.
- Daily Activities: You can and should continue with most of your normal activities while wearing the monitor. This provides your healthcare provider with information about how your heart functions during your typical daily routine.
- Return to Clinic: After the monitoring period is over, you’ll return to the clinic to have the device removed. The data recorded by the monitor will then be analyzed by your healthcare provider.
- Follow-Up: Based on the results, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to discuss the findings and any further steps or treatments that may be needed.
Since the test is non-invasive and the device is portable, it allows for the monitoring of your heart without the need for a hospital stay. This convenience is one of the reasons why Holter monitoring is a commonly used tool for diagnosing heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Avoid Water Activities: Since the Holter monitor is an electronic device, it’s important to keep it dry. Avoid swimming, bathing, or showering while wearing the monitor. Some newer models might be water-resistant, but it’s best to confirm with your healthcare provider.
- Physical Activities: You can engage in regular physical activities unless instructed otherwise by your doctor. However, excessive sweating might loosen the electrodes, so it might be wise to avoid extremely strenuous exercises.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Try to avoid areas with strong electromagnetic fields, such as metal detectors or high-powered electrical equipment, as they can interfere with the monitor. For example, avoid flying.
- Sleep Considerations: Wear the monitor while sleeping. It can be helpful for the doctor to see your heart’s activity during sleep. If the monitor is uncomfortable, try to position it in a way that doesn’t disrupt your sleep.
- Medications and Diet: Continue taking any prescribed medications unless your doctor advises otherwise. There are generally no dietary restrictions, but it’s a good idea to keep your diet consistent with what you would normally eat.
- Diary of Activities and Symptoms: You will likely be asked to keep a diary of your activities and any symptoms you experience while wearing the monitor (such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or palpitations). This helps correlate specific activities or times with any changes in your heart rhythm.
- Clothing Considerations: Wear comfortable clothing that allows easy placement of the monitor and electrodes. A shirt that buttons in the front can be more convenient for wearing and adjusting the monitor.
- Avoiding Skin Irritation: The adhesive used to attach the electrodes might cause skin irritation for some people. If you have sensitive skin, mention this to your healthcare provider.
Remember, the more typical your activities are during the monitoring period, the more representative the data will be of your heart’s usual activity. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. If you have any specific concerns or questions about your activities during the Holter monitoring, it’s best to discuss them with your healthcare provider.